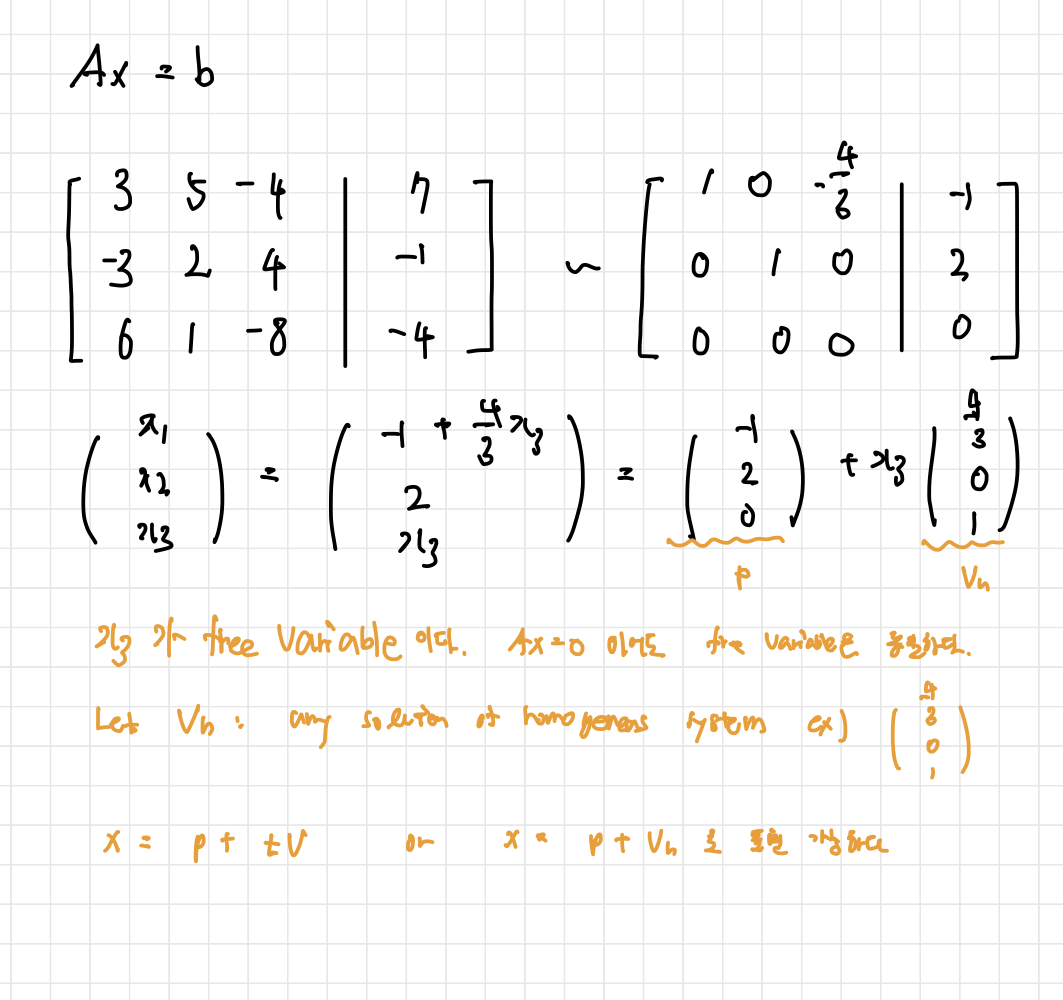Linear Equation
\[\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\]equivalent if the system has same solution set
A system of linear equations has either
no solution or
unique solution or
inf many solution
coefficient matrix
augement matrix
Elementary row operations
- scaling
- interchaning
- scaling
row equivalent
- coefficent matrix 에 row equivalnet ⇒ row operations 거치면 같다
- augmented matrix에 row equivalent ⇒ row operations해도 solution set 동일하다
EF vs REF vs RREF
EF
모든 원소가 0인 행렬 맨 아래로
leading entry of a row shoud be in a column to the right of the leading entry of the row above it.
REF
(leading 1 등장)
0이 아닌 원소를 갖는 행에서 맨 처음 나오는 0이 아닌 수는 1이어야 한다. 이러한 1을 선도 1(leading one)이라고 한다.
모든 원소가 0인 행은 행렬의 맨 아래로 내려가야 한다.
0이 아닌 원소를 갖는 연속된 두 행은 해당 행의 leading 1이 윗 행의 leading 1보다 오른쪽에 있어야 한다.
RREF
REF +
- Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entroy in its column
leading variable
free variable
Uniqueness of the reduced echelon form
- inconsistent
[ 0000 b ] b≠ 0 : augement column is a pivot column in an echelon form
- consistent : pivot in every row in coffecient part
- no free variable
pivot in every column in coefficnet part in echelon form
(이 말이 사실 linear independent와 동일하다)
number of pivot columns are same as number of variables
- free variable
- no free variable
How to make RREF form
- forward phase (making REF)
- backward phase (making RREF)
Homogeneous
\[Ax=0\]at least trivial solution x = 0
only trivial solution when A has inverse : determinant ≠ 0
non - homogeneous
unique solution → pivot in every column (correct)
| 이때는 [ 00000 | b ]일 수 없다. consistent해야하니깐 |
pivot in every column → unique solution (incorrect)
| [ 0000 | b]꼴이여도 pivot in every column 이다 |
homogeneous
unique solution ←→ pivot in every column (correct)
| [ 00000 | b ] 불가능 ⇒ 즉 always consistent due to trivial solution |
| [ 00000 | 0 ] 이경우에는 pivot이 없다. |
따라서 unique solution이 없으려면 free variable이 없어야한다.